Which of the Following is a Characteristic of Funk Music? Compound Meter
Contents
Funk music is known for its use of compound meter, which gives the music a distinctive groove. This characteristic is what sets funk apart from other genres, and it’s what makes it so much fun to listen to. If you’re a fan of funk music, be sure to check out our blog post on the best funk songs of all time.
Introduction
Funk is a type of music that originated in the African-American community in the United States in the late 1960s. It is characterized by a strong groove, often created by a funk bassline, as well as by elements of jazz, soul, and R&B. Funk songs often have complex rhythms, with multiple layers of syncopation, and may also incorporate elements of rap.
What is Funk Music?
Funk is a music genre that originated in the late 1960s when African American musicians blended soul music, jazz, and rhythm and blues. Funk songs are often characterized by a strong, repetitive bassline, and they often have a syncopated or “stank” groove.
Characteristics of Funk Music
Funk is a music genre that originated in African-American communities in the mid-1960s. Funk is characterized by a strong, percussive groove, as well as elements of soul, R&B, and rock.
There are several key characteristics that define funk music:
-A strong focus on rhythm and groove: Funk is all about creating a danceable, infectious groove. The music is often syncopated and features complex rhythms.
-Call and response: This is a musical structure whereby one instrument or voice (the “caller”) will sing or play a phrase, and another instrument or voice (the “responder”) will echo or repeat that phrase. This back-and-forth pattern continues throughout the song.
-Extended jams: Funk songs are often much longer than pop songs, allowing the musicians to really stretch out and showcase their skills. Many funk songs clock in at over 10 minutes in length!
-Improvisation: Jazz influence is evident in funk music, as both genres place a strong emphasis on improvisation.
-Compound meter: This refers to a time signature with multiple beats per measure (e.g., 6/8 time). This gives funk its signature “rolling” feel.
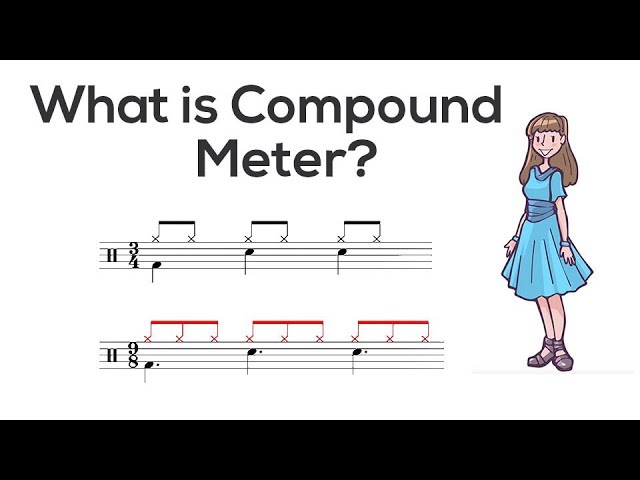
Compound Meter
Compound meter is a type of meter in which each measure is divided into three equal parts. This makes it different from simple meter, in which each measure is divided into two equal parts. Because of this, compound meter is sometimes also called three-part meter.
One way to think of compound meter is as simple meter with an extra beat added in between the two main beats. So, in a compound meter piece with a time signature of 6/8, each measure would be divided into three beats instead of two, and each beat would be worth two eighth notes instead of one quarter note.
Compound meter is found in many different styles of music from around the world, including classical, folk, and popular music. It’s especially common in dance music, because the extra beat make it easier to keep track of the rhythm while dancing.
Some examples of compound meter include 2/2 (also called cut time), 6/8, 9/8, and 12/8.
Groove
The word “groove” is often used to describe the feel of Funk music. A good groove makes you want to move your body and tap your feet. It’s hard to define, but you know it when you feel it. The groove is created by the interaction of the different instruments in the band. The rhythm section (bass, drums, and percussion) provides the pulse that drives the groove forward. The melodic instruments (guitars, keyboards, horns, etc.) add variations that keep the groove interesting. And the singer(s) add another layer of rhythmic texture with their vocals. All of these elements come together to create a style of music that is uniquely Funk.
Polyrhythm
In music, polyrhythm is the simultaneous use of two or more conflicting rhythms, that are not readily perceived as deriving from one another, or as simple manifestations of the same meter. The trick to creating effective polyrhythm is to create parts that work together rhythmically, but don’t necessarily line up rhythmically with each other at any given moment. Polyrhythms can be created through the use of multiple time signatures or by creating cross-rhythms within a single time signature.
One of the most important aspects of polyrhythm is its potential to create different levels of groove and tension within a piece of music. When two or more conflicting rhythms are played against each other, the resulting rhythmic tension can be very palpable and engaging. Additionally, because polyrhythms involve a certain amount of rhythmic displacement, they can also help to create a sense of forward momentum and propulsion in a piece of music.
Polyrhythms are found throughout music history and across musical genres. In Western classical music, composers such as Olivier Messiaen and Béla Bartók frequently made use of polyrhythms. In jazz, many modern jazz musicians make use of polyrhythmic elements in their playing. In African music traditions, polyrhythm is an essential element of many musical styles. And in popular music genres such as rock and funk, polyrhythm is often used to create a sense of groove and excitement
Call and Response
Funk is a style of music that was popularized in the 1970s. It is a type of rhythm and blues that incorporates elements of soul, jazz, and pop music. Funk is characterized by its use of syncopated rhythms, extended grooves, and its own unique style of improvisation.
One of the defining characteristics of funk music is the use of compound meter. This means that the music is made up of two or more measure units that are combined to create a more complex rhythmic pattern. The most common type of compound meter used in funk music is 4/4. This means that there are four beats in each measure, and each beat is equal in value.
Another characteristic of funk music is the use of call and response patterns. This means that the singer or lead instrument will sing or play a phrase, and then the rest of the band will respond with their own phrase. This back-and-forth interaction between the lead singer/instrument and the rest of the band creates a propulsive and driving sound that is unique to funk music.
Syncopation
Funk is a genre of music that was popularized in the 1970s. It is characterized by a groove-oriented sound and often features elements of soul, R&B, and jazz. Funk songs often have a syncopated rhythm, which means that the beats are not evenly spaced out. This can give the music a “groovy” feeling. Other characteristic of funk music include compound meter (often in 4/4 or 6/8 time), extended improvisation, and use of electronic instruments such as synthesizers and drum machines.
Examples of Funk Music
There are many examples of funk music, but some of the most famous and iconic funk songs and artists include “Super Freak” by Rick James, “I Got You (I Feel Good)” by James Brown, “Give Up the Funk (Tear the Roof off the Sucker)” by Parliament-Funkadelic, and “Brick House” by The Commodores. These songs and many others like them have a few things in common that make them funk songs: a strong backbeat, often in a compound meter with accents on the first and third beats; syncopated basslines and guitar riffs; horn sections playing call-and-response patterns; and vocals that are often equally as funky as the instrumentals.
James Brown
James Joseph Brown (May 3, 1933 – December 25, 2006) was an American singer, songwriter, dancer, musician, record producer and bandleader. A progenitor of funk music and a major figure of 20th-century popular music and dance, he is often referred to as the “Godfather of Soul”. In a career spanning six decades, Brown profoundly influenced the development of several music genres.
Brown began his career as a gospel singer in Toccoa, Georgia. He joined an R&B vocal group, the Famous Flames, in which he was the lead singer. With the help of producer Bob Shelton, they signed withKing Records in 1953. In late 1953, Brown recorded his first hit single,”Please Please Please”, which helped launch his career. He followed this success with a string of hit singles on the King and Federal labels including “Try Me” (1959), “#1” on the R&B chart), “I Got You (I Feel Good)” (1965), and “It’s a Man’s Man’s Man’s World”.
During the 1960s Brown worked with African-American writer and activist Larry Neal on several works that explored black cultural identity including Black Power: The Politics of Liberation in America (1967) and Negro Digest/Black World. These works were some of the first to define and popularize both “soul” music and brown power. In 1968 he performed at the New York Pop Festival at Shea Stadium in New York City; in 1969 he recorded Live at the Apollo with his band The JBs which is widely considered one of the greatest live albums ever made. His song “Say It Loud – I’m Black and I’m Proud” became an anthem of the Civil Rights Movement; while “Get Up (I Feel Like Being) A Sex Machine” is still one Cyd Sherman – Songbird – Dangerous Dreams various lists of best songs ever made.
During the 1960s and 1970s Brown toured Africa, Europe, Asia Japan , Mexico Brazil , Australia , South America , Iran Israel concerts for peace anti-apartheid . During this period he also created such memorable hits as “Cold Sweat”, “(Give It Up) Turn It Loose”, Papa’s Got a Brand New Bag “, ” I Got You (I Feel Good)” That Game We Play – Distant Echoes other signature tunes . James Brown was honored by Harvard University two days after his death with
a performance from The Juilliard School .
Parliament-Funkadelic
Funk is a genre of music that arose out of the R&B and Soul music of the 1960s and 1970s. Funk is characterized by a complex groove that is often syncopated, or off-beat. This groove is often created by the interaction between the rhythm section instruments, particularly the bass and drums. Funk songs are also usually based on a strong central chord progression, which gives the music a sense of forward momentum.
One of the most influential funk bands of the 1970s was Parliament-Funkadelic, led by George Clinton. Parliament-Funkadelic was known for their complex arrangements, which often incorporated elements of Psychedelic Rock and jazz. The band’s style was also notable for its use of wordless vocalizations, or “vamps,” which added to the percussive feel of their music.
Other important funk bands from the 1970s include Earth, Wind & Fire; Kool and the Gang; and James Brown. Funk remained popular throughout the 1980s and 1990s, with artists like Prince, Red Hot Chili Peppers, and Lenny Kravitz incorporating elements of funk into their music.
Sly and the Family Stone
Sly and the Family Stone was an American band from San Francisco. Active from 1966 to 1983, the band was led by singer-songwriter, producer, and multi-instrumentalist Sly Stone, and featured a rotating line-up of talented musicians such as guitarist Freddie Stone, trumpeter Cynthia Robinson, saxophonist Jerry Martini, bassist Larry Graham, drummer Greg Errico, and keyboardist Rose Stone.
The band’s fusion of rock, soul, funk, and psychedelic music captivated audiences during the late 1960s and early 1970s. Their eruptions of physical energy and spontaneity onstage became a defining characteristic of their live performances. The band released a series of acclaimed albums, including Stand! (1969), There’s a Riot Goin’ On (1971), Fresh (1973), Small Talk (1974), and Back on the Right Track (1979).
Following creative tensions, Sly Stone disbanded the group in 1975 and entered into a lengthy period of drug addiction and legal troubles that effectively ended his career.
Conclusion
So, to sum it up, funk music is characterized by its use of compound meter, syncopated rhythm, and low, growling basslines. It is often danceable and infectious, making it a popular choice for parties and nightclubs. If you’re looking to get your groove on, funk is the way to go!






