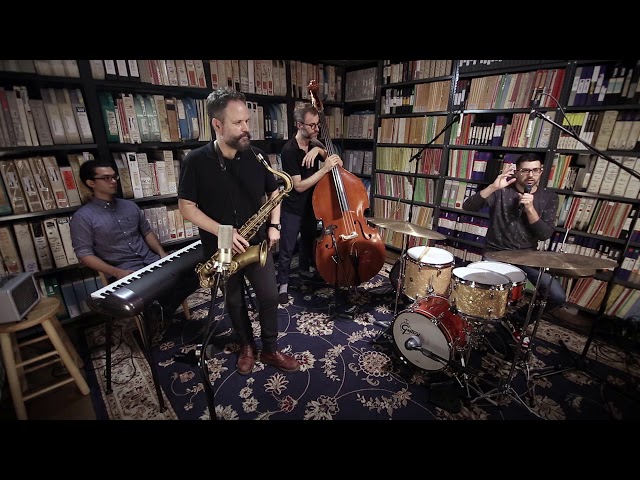
The Importance of the Instrument in Jazz Music

Contents
The instrument is one of the most important aspects of jazz music. It can convey the emotions and ideas of the composer and performer, and connect the listener to the music.
The instrument in Jazz
The instrument is very important in Jazz music. It is the foundation of the music. The instrument can be anything from a piano to a guitar to a saxophone. It is the melody and the harmony that make up the Jazz sound. The instrument is what makes the music interesting and unique.
The piano
The piano is an important instrument in Jazz. It is used to set the harmony and to provide a solo voice. The piano has a unique history in Jazz. It was not always used in Jazz music, but it became an important part of the sound in the early 1900s.
The first pianists in Jazz were not soloists, but they played an important role in the band. They provided the harmony and they kept the time. The first pianists were also composers and arrangers. They wrote songs and arranged them for the band. The first pianists in Jazz were Jelly Roll Morton and Fats Waller.
As Jazz evolved, the piano became more important as a solo instrument. Pianists began to improvised and to play solos. The best known pianist from this era is Duke Ellington. He was a composer, arranger, and bandleader as well as a pianist. His style was very melodic and he had a great touch on the piano.
Other important pianists from this era include Bill Evans, McCoy Tyner, and Herbie Hancock. These pianists took different approach to soloing on the piano. Bill Evans was very influenced by classical music. He created a new sound for jazz piano that was very different from what had come before him. McCoy Tyner played with more of a blues feel. He also used more extended chords than other jazz pianists which gave his solos a unique sound. Herbie Hancock experimented with different sounds on the piano including electric keyboards
The saxophone
The saxophone is one of the most important and prevalent instruments in jazz music. It was invented by Belgian musician Adolphe Sax in the 1840s, and was originally used as a military band instrument. But in the early 1900s, jazz musicians began to experiment with the saxophone and it quickly became an integral part of the genre.
There are many different types of saxophones, but the most common ones used in jazz are the alto, tenor, and baritone saxes. The alto sax is the highest-pitched of the three and has a range of about two octaves. It’s often used as a lead instrument because of its high range and ability to play melodies with a lot of emotion. The tenor sax is slightly lower-pitched than the alto and has a range of about two and a half octaves. It’s often used as a solo instrument because of its rich, full sound. And finally, the baritone sax is the lowest-pitched of all three and has a range of about two octaves. It’s often used as an accompaniment instrument because of its deep sound.
No matter what type of saxophone you’re playing, though, there are some basic jazz techniques that all players should know. These include bending notes (changing the pitch by vibrating your lips), vibrato (a rapid shaking of the instrument), growling (making a raspy sound by constricting your throat), altissimo (playing very high notes), and glissando (sliding up or down between notes).
If you’re interested in learning how to play jazz saxophone, there are many great resources available online and in print. But one of the best ways to learn is by listening to great jazz musicians and transcribing their solos. This will not only help you learn how to play their licks and phrases, but it will also give you a better understanding of how to create your own solos.
The trumpet
In jazz, the trumpet is one of the most important instruments. It has a wide range, a beautiful sound, and can be very versatile. It can be used to play both lead and rhythm parts.
The trumpet has been an important part of jazz since the early days of the genre. It was used by Louis Armstrong and other early jazz pioneers to create a new style of music that was apart from the European classical tradition. The trumpet has since become one of the most popular and versatile instruments in jazz, capable of playing a wide range of styles.
There are many different types of trumpets available, each with its own unique sound. Choosing the right trumpet for your style of playing is important, as it will make a big difference in how you sound. You should also consider your budget when choosing a trumpet, as they can vary widely in price.
No matter what type of trumpet you choose, though, remember that it is one of the most important instruments in jazz music!
The different styles of Jazz
Jazz music is a genre that is heavily reliant on the instruments used. The most popular instruments in Jazz include the saxophone, trumpet, and piano. Each instrument brings its own unique sound to the genre. For example, the saxophone is often used for its mellow sound, while the trumpet is used for its more lively sound.
Bebop
Bebop is a style of jazz developed in the early and mid-1940s in the United States, which features songs characterized by fast tempo, complex chord progressions with rapid chord changes and numerous changes of key, instrumental virtuosity, and improvisation based on a combination of harmonic structure, the use of scales and intermittent passages.
Hard bop
The mid-1950s saw the hardening of the bebop sound, which incorporated influences from R&B and blues. The quintessential hard bop band was the Horace Silver Quintet, which combined blues progressions, gospel harmonies, and tidal waves of energy. Tenor titan Sonny Rollins led a number of small groups that explored the outer reaches of hard bop while retaining much of the style’s earthiness; his groups with trumpeter Clifford Brown and pianist Thelonious Monk are considered to be among the finest ever.
Modal jazz
Modal jazz is a jazz composition style that began in the late 1950s with Miles Davis’s composition “Milestones” and John Coltrane’s album My Favorite Things.
In jazz, mode is the scale from which a piece of music derives its melody. In modal jazz, a composer or improviser will choose a mode or scale and use it as the basis for their melody and improvisation. The choice of mode gives the piece of music its character and helps to define the style of jazz that it belongs to.
The most common modes used in modal jazz are:
-Major Scale
-Minor Scale
-Dorian Mode
-Phrygian Mode
-Lydian Mode
-Mixolydian Mode
The history of Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It is a genre of music that is characterized byswing and blue notes, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and improvisation. Jazz has been influenced by African American folk music, European military band music, and the blues.
The origins of Jazz
Most historians agree that Jazz originated in New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th or early 20th century. Jazz is a combination of African and European musical traditions. The African influence is most evident in the use of blue notes, call-and-response patterns, and polyrhythms. The European influence is most evident in the use of harmony and instruments such as the piano and trumpet.
The exact origin of the word Jazz is unknown, but it is thought to be derived from the French word “jaser” which means “to chatter or talk.” Jazz was originally a term used to describe the music of African American musicians. Over time, the term came to be associated with a particular style of music.
Jazz was originally performed by small groups of musicians playing informal concerts in bars and clubs. These early performances were often improvised and were heavily influenced by the blues. As Jazz became more popular, it began to be performed by larger groups in more formal settings such as concert halls and theaters.
Today, Jazz is enjoyed by music lovers all over the world. It has exerted a powerful influence on other genres of music such as rock and roll and hip hop.
The development of Jazz
While its origins are somewhat murky and debatable, it is generally agreed that Jazz began to take shape in the early 20th century in New Orleans, Louisiana. A melting pot of cultures, New Orleans at the time was known for its freewheeling atmosphere and laissez faire attitude, which provided the perfect breeding ground for a new style of music to emerge.
Early Jazz was a blend of African and European musical traditions, with a healthy dose of improvisation thrown in. The African influence is most evident in the use of blue notes (flattened or played slightly below the note), call-and-response patterns, and the use of swing (a rhythmic technique that gives the music a hypnotic, swaying feel). The European influence isheard in the use of horns and other brass instruments, as well as in the structure of some Jazz tunes (many early Jazz tunes were based on popular songs or “tin pan alley” tunes of the day).
As Jazz evolved, other influences began to make their way into the music as well. Latin American rhythms and harmonies began to find their way into Jazz in the 1930s and 1940s, thanks to musicians such as Dizzy Gillespie and Machito. And bebop, a faster and more complex style of Jazz that emerged in the 1940s, was heavily influenced by Classical music (another result of Gillespie’s experiments with blending styles).
Jazz has continued to evolve since its humble beginnings in New Orleans’ red light district. Today’s Jazz musicians are influenced by all kinds of music, from Rock to Hip Hop to World Music. But no matter how far it has come or how many different styles it has absorbed along the way, Jazz will always retain its roots in improvisation and creativity.
The golden age of Jazz
The golden age of Jazz is often considered to be from the mid-1920s to the early 1940s. During this time, jazz music was evolving rapidly, and many different styles were being developed. This was also a time when many of the most famous jazz musicians were active, such as Louis Armstrong, Duke Ellington, and Benny Goodman.
After the Second World War, jazz began to change again, as musicians started to experiment with different sounds and styles. This period is sometimes known as the post-war era or the bebop era. Some of the most important developments during this time were the rise of cool jazz and hard bop.
In the late 1950s and 1960s, jazz became more experimental, with artists such as Miles Davis and John Coltrane pushing the boundaries of what was possible with the genre. This period is known as the avant-garde era or free jazz.
Jazz has continued to evolve since then, with new styles and subgenres appearing all the time. However, the impact of those early years is still felt today, and many of those original musicians are still revered as legends of the genre.
The influence of Jazz
Jazz Music has been around for over a century and has been constantly evolving. The genre has been influential in the development of other genres of music. Jazz has also been known to be instrumental in the civil rights movement. The importance of the instrument in jazz music cannot be understated.
On American culture
Jazz is often considered one of America’s greatest cultural achievements. The genre has its roots in the African-American experience, and its popularity has spread around the world. Jazz has had a profound impact on American culture, influencing everything from fashion to film.
Jazz music was born in the early 20th century, in the African-American communities of New Orleans. The style was a blend of African and European musical traditions, and it quickly caught on with other black communities in the United States. Jazz became popular among white Americans in the 1920s, when bandleaders like Paul Whiteman began to experiment with the genre.
By the 1930s, jazz was an established part of American culture. The decade saw the rise of Swing, a jazz subgenre that enjoyed immense popularity. Swing bands like Benny Goodman’s orchestra helped make jazz mainstream, and performers like Billie Holiday and Ella Fitzgerald became household names.
The 1940s marked a watershed moment for jazz, as bebop emerged as a new style. Bebop was faster and more complex than Swing, and its popularity signaled a shift in the demographics of jazz audiences; from this point on, jazz would be largely associated with African-Americans. The 1950s saw the rise of cool jazz, which boasted a more restrained sound than bebop; Miles Davis’ 1959 album Kind of Blue is considered one of the finest examples of cool jazz.
In the 1960s, jazz began to splinter into different subgenres; free jazz abandoned traditional harmonic structures altogether, while fusion sought to meld jazz with rock music. These new styles alienated some listeners, but they also helped to bring about a renewed appreciation for older styles of jazz. Today, there is no single definition of what constitutes “jazz”; instead, the genre encompasses a wide range of sounds and styles. But whether it’s traditional or experimental, straight-ahead or avant-garde, one thing remains constant: Jazz is one of America’s greatest musical accomplishments.
On popular music
Jazz music is often credited with influencing the development of popular music genres such as blues, rock and roll, and hip hop. Jazz has also been described as a ” melting pot” genre, because it borrows elements from other musical styles.
Jazz began to achieve widespread popularity in the early 1920s, when musicians such as Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington began to gain popularity with mainstream audiences. Jazz quickly became one of the most popular genres of music in the United States, and by the 1930s, it had spread to Europe and Asia.
One of the biggest reasons for jazz’s widespread appeal is its versatility; jazz can be played as either a solo or ensemble form, and it can be adapted to fit any number of musical settings. For example, jazz bands often play at dance clubs, conventions, and wedding receptions.
In addition to its popularity with audiences, jazz has also been praised by critics for its originality and creativity. Jazz is considered to be one of the most important musical genres of the 20th century, and its influence can still be heard in popular music today.