The Musical Features of Blues Music
Contents
The blues is a genre of music with its roots in the African-American experience. The blues has been a major influence on other genres of music, including jazz, rock, and country. The blues is characterized by its use of blue notes, call-and-response patterns, and its focus on the expression of emotions.
The Origins of the Blues
The blues is a genre of music that originated in the African-American communities in the American South in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The style is a fusion of African and European music. The term “blues” refers to the blue notes in the music, which are notes that are sung or played at a lower pitch than the major scale.
The Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta is a region of the U.S. state of Mississippi that lies between the Mississippi and Yazoo rivers. It is one of the most historic and culturally significant regions in the country, and it has been home to many important figures in American music, including W.C. Handy, Muddy Waters, and John Lee Hooker. The Delta is also the birthplace of the blues, a genre of music that has had a profound impact on American culture.
The blues began in the late 19th century, when African Americans were working in the cotton fields of the Mississippi Delta. They would sing work songs to keep themselves motivated, and these songs would often incorporate elements of African American spirituals and folk music. Over time, these work songs developed into a more refined form of music, with intricate melodies and expressive lyrics that reflected the hardships and experiences of African Americans in the South.
The blues quickly spread beyond the Mississippi Delta, and by the early 20th century, it was being performed by musicians all over the country. The genre would go on to exert a significant influence on other forms of American music, including jazz, rock ‘n’ roll, and country.
The Piedmont
The Piedmont is a hilly region located in the eastern United States. The name is derived from the French word for “foot of the mountain,” and it includes the state of Virginia, as well as parts of North and South Carolina. The Piedmont region is characterized by its rolling hills, red clay soil, and mild climate. The area was first settled by European colonists in the seventeenth century, and it quickly became a center for tobacco production.
In the early twentieth century, the Piedmont became known for its vibrant music scene. The Piedmont style of blues is characterized by its use of syncopated rhythms, or “riffs.” This type of blues often includes a guitar solo played over a simple chord progression. The Piedmont style is also known for its “ragged” sound, which is created by pentatonic scales and irregular phrasing.
The Piedmont region was home to many influential blues musicians, including Blind Lemon Jefferson, Blind Boy Fuller, and Reverend Gary Davis. These musicians created a sound that would eventually be adopted by blues musicians all over the world.
The Characteristics of the Blues
The blues is a style of music that originated in the African-American communities in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It is characterized by blue notes, call-and-response patterns, and specific chord progressions. The blues has influenced a wide range of other musical genres, including gospel, jazz, R&B, and rock and roll.
The 12-bar blues
The 12-bar blues is the most commonly used blues form. Though it can be (and has been) adapted to different meters, it is most commonly in 44 time, which sets up a repeating pattern of three chords over a duration of 12 bars ( bars are measures of time). The basic form looks like this:
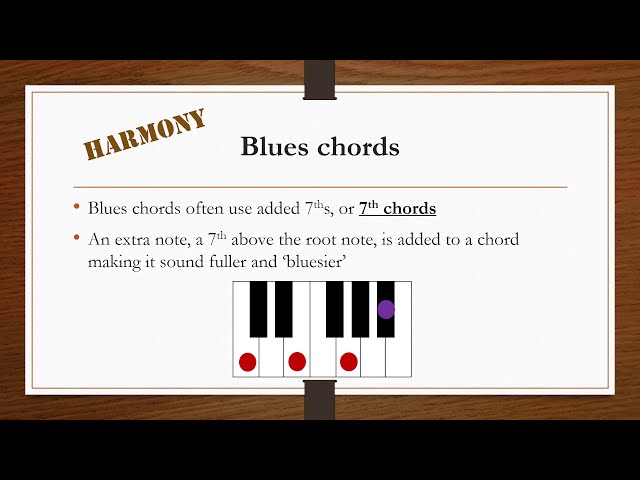
One chord is played for two bars, followed by a different chord for one bar, returning to the first chord for two more bars. This repeats until all 12 bars are finished. Chords are usually chosen from a I-IV-V progression, which in the key of C would be C-F-G. The IV and V chords are sometimes replaced with their minor equivalents, giving a I-IV-V progression in the key of C of C-F-G-C-Cmaj7-F7-G7.
The use of blue notes
One of the most distinctive features of blues music is the use of blue notes. These are notes that are played or sung at a slightly lower pitch than expected, and they give blues music its characteristic “sad” sound. While Western music generally uses a major or minor scale, blues music often uses a “blues scale” which includes both major and minor notes. This gives blues music its unique sound and helps to create the feeling of melancholy that is so characteristic of the genre.
The call and response format
The call and response format is a musical form that is characteristic of blues music. The format is simple: one person sings or “calls”, and another person or group responds. The response can be either in the form of words, or in the form of musical phrases.
The call and response format was probably derived from the African tradition of storytelling. In African tradition, one person would tell a story, and others would respond with comments or questions. This format allowed for a back and forth exchange between the storyteller and the audience, which helped to keep everyone engaged in the story.
The call and response format is also found in other types of music, including gospel, jazz, and hip hop.
The Influence of the Blues
The blues is a musical genre that originated in the African-American communities in the Deep South of the United States around the end of the 19th century. The genre developed from the music of the African-American slaves who were brought to the American South to work on the plantations. The blues is a unique and powerful form of music that has influenced many other genres of music, including jazz, rock and roll, and hip hop.
On other genres of music
The blues has been a major source of inspiration for musicians in other genres since its inception. Its simple forms and rhythm have influenced everything from rock and roll to hip hop, and its use of improvised lyrics has had a profound effect on the development of lyrical composition in popular music. In addition to its direct influences, the blues has also indirectly inspired many other genres through its influence on the artists who created them.
On popular culture
The blues has been a major influence on later American and Western popular music, finding expression in jazz, big band, rhythm and blues, rock and roll, and country music, as well as in the telltale duende of flamenco. Although blues music was originally conceived and performed by African Americans in the American South, it quickly spread north through the Mississippi Blues Trail, finding fertile ground in Chicago at the famed Maxwell Street open-air market. From there it went on to shape the sound of popular music around the world for generations to come.






